

























Disk array can effectively improve the reliability and performance of the storage system, but there is a significant disadvantage, that is, due to the simultaneous use of multiple devices (disks(1), resulting in a reduction in reliability (from the point of view of the probability: N devices of the reliability of a device 1/N).
RAID (Redundant array of inexpensive disk) was created to solve this problem. RAID improves the reliability of a disk array by adding redundant disks to the array. The so-called redundant disk, that is, the disk is not used to store the actual data, but used to store some redundant information, and these redundant information can be used when necessary to carry out effective data recovery, thereby increasing the reliability of the disk array, translated into Chinese should be called the redundant array of inexpensive disk.
Before the advent of RAID6, RAID has been from RAID0 to RAID5 six versions. So we have so many RAID methods, providing a considerable level of reliability protection, why do we still need RAID6? Here, we here first comparative study of a few more representative RAID methods.
Disk redundancy family overview
Currently the most widely used, support the largest number of devices RAID mode is mainly RAID0, RAID1 and RAID5
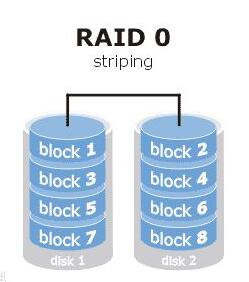
(1) no redundancy (RAID0): RAID0 actually can not be considered as a real RAID technology, it is only the realization of the disk array to store the data of the band distribution. Although it improves the performance of large-scale data access, but RAID0 does not have the function of redundancy fault tolerance, because it is not redundant, so it can be said that the RAID0 is a misnomer here!
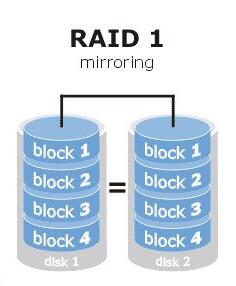
(2) mirroring (RAID1): RAID1 also realizes the bandwidth distribution of data, unlike RAID0 is that in the data written to a disk, at the same time in another disk to do the corresponding mirror. Therefore, although RAID1 data fault tolerance, but its utilization of the disk is relatively low, only 50%.
(3) parity (RAID5): relative to RAID1 comparison, RAID5 is only a single disk redundancy error correction function, but has greatly improved the effective utilization of the disk. RAID5 (4D + P) as an example, the use of four disks to store the data bits, the use of a disk to store the parity bit. The basic principle is this: according to the striped data 4D (using four bits of data) to generate a parity information, stored in the fifth disk.
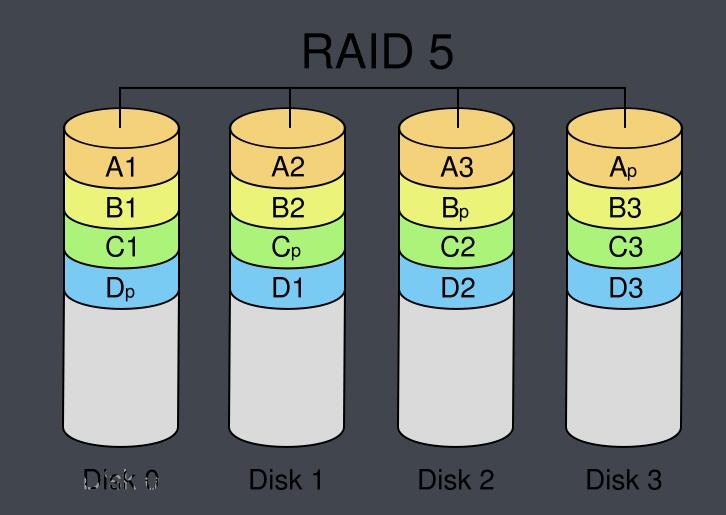
Generate P parity bit of the formula is generally this.
P = D1 ⊕ D2 ⊕ D3
P is the parity bit, D1 ~ D3 represent three data bits, ⊕ represents the heterodyne operation.
It can be seen that when D1, D2, D3 in the rest of a data loss, you can use the rest of the three data bits and the parity bit P to recover, the specific recovery formula is as follows.
For example, when D1 is lost, D1 = D2 ⊕ D3 ⊕ P
At the same time, you can see that when two fast disk failure, RAID5 can not be recovered.
RAID6: Breaking through the limitations of disk redundancy
RAID5 has provided a degree of reliability, but also sacrificed a certain amount of read speed. Especially in the RAID reconstruction operations, a large number of data read and write operations to increase the burden on the hard disk, the old hard disk is more prone to failure.RAID5 limitations are also manifested in the RAID5 only in the case of a hard disk failure to repair the data, if two hard disk failures at the same time, RAID5 can not help.
Previously, the two disks at the same time bad situation is a small probability of events, almost impossible to happen. But recently, with the fiber-optic (FC) disk and SATA disk capacity and density continue to increase, so that the reconstruction time of RAID 5 also continue to increase. The probability of two hard disk damage at the same time has also increased dramatically, in the enterprise storage, this risk must be taken seriously. So RAID6 should be born.
RAID6 with RAID5 is the biggest difference in the basis of RAID5 in addition to the P parity bit, but also added the second parity bit Q bit. RAID6 (6D + 1P + 1Q) as an example, this system requires 8 hard disk, 6 of which are used to store the data, 1 used to store the P parity bit, 1 used to store the Q parity bit. Of course, I have to emphasize again, is not a specific independent disk all used to store P parity information, another Q parity information. Rather, for a certain bit group (6 data bits + P bits + Q bits), using some kind of principle, 6 disks to store the data bits, 1 disk to store the P bits, 1 disk to store the Q bits.
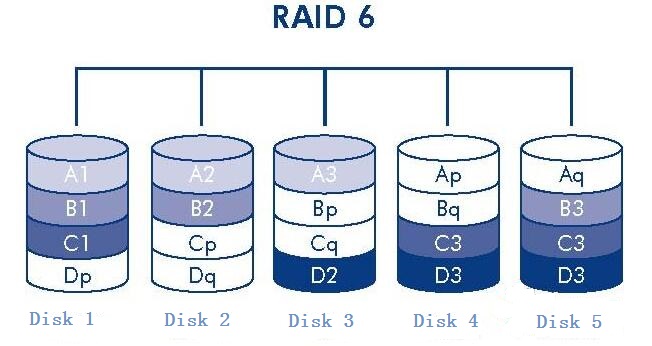
The mathematical principle is as follows.
Generation of check digit.
P = D1 ⊕ D2 ⊕ D3
Q = GF(D1) ⊕ GF(D2) ⊕ GF(D3)
D1~D3:Striped data
P:P parity bit
Q:Q parity bit
⊕:Different-or operation
GF(D1):Galois Field transformation of D1 bits.
When there is a data error or loss on one disk, the recovery method is the same as RAID5, without using Q parity bit. When two disks on the data error or loss of time, the recovery method is: the use of the above given P, Q generation formula, the system of joint equations, regardless of whether the damaged data include P or Q, always be able to solve the loss of two of the data.
Comparison of data security between RAID6 and RAID5.
For the same eight disks, data utilization is the same 75%, but respectively with RAID5 and RAID6 for the construction of the array to compare the situation. One with two independent RAID5 (3D +1P) build; the other with RAID6 (6D +1P +1Q) build, the application of Bernoulli (Bernoulli) probability distribution is analyzed as follows (assuming that the probability of failure of a single disk in 10 years is):: two independent RAID5 (3D +1P) build; the other with RAID6 (6D +1P +1Q) build, the application of Bernoulli (Bernoulli) probability distribution is analyzed as follows (assuming that the probability of failure of a single disk in 10 years is).
The probability analysis of data security of the system constructed by two independent RAID5 (3D+1P).
The data of this system is safe in three cases.
1. The probability that none of the 8 disks are damaged is
2. The probability that only one of the eight disks is damaged is
3. the probability that one disk is damaged in each of two independent RAID5(3D+1P) systems is
So, the total probability of data security of two independent RAID5(3D+1P) constructed system is
The probability of data security for a system built with RAID6 (6D+1P+1Q) is analyzed as follows.
1. the probability that none of the 8 disks are damaged is [same as the previous system].
2. If only one of the 8 disks is damaged, the probability is [same as the previous system].
3. the probability that two of the eight disks are damaged is [same as the previous system].
So, the total probability of data security for a RAID 6 (6D+1P+1Q) system is
Practical point, assuming that the probability of failure of a single disk in 10 years is , then the system built with RAID5, ten years without failing the probability of security is 99.881629%; compared with the system built with RAID6, ten years without failing the probability of security is 99.994607%.
Visible, RAID6 data security level is quite high. Of course, the security of RAID5 is also quite good. From the above data looks, the two are not very different. But for the probability of failure RAID5 is 0.118371%, RAID6 is 0.005393%. This seems to be a big improvement. With the increasing capacity of the disk leads to the increase in the probability of data errors. The gap between the two will further increase, RAID6 advantage is more obvious. When the disk capacity increased to more than 20TB, RAID6 security than RAID5 has been about 1000 times higher.
Summary
The differences between RAID6 and RAID5 are summarized as follows.
RAID6 is an improvement in RAID5, RAID6 can not only in the case of a disk offline will be able to recover the data (using the same checksum and RAID5), and because of the use of two disks as the error correction disk, so it can cope with the situation of two disks offline at the same time.
In the case of using large blocks of data, RAID6 random read performance is very good; because not only to write the parity data on each hard disk and to write data on a special parity hard disk, RAID6 random write performance is very poor. RAID6's sustained write performance is average, but it performs well when using small blocks of data.
Overall, RAID6 has faster read performance, higher fault tolerance. But at the same time, RAID6 also has the disadvantage of slow write speed, RAID controller in the design of more complex, more expensive.
If you have requirement of network equipments, please contact us www.hi-network.com (Email: [email protected])
 Горячие метки:
Сервер на сервере
Рейд в аэропорту
Горячие метки:
Сервер на сервере
Рейд в аэропорту