















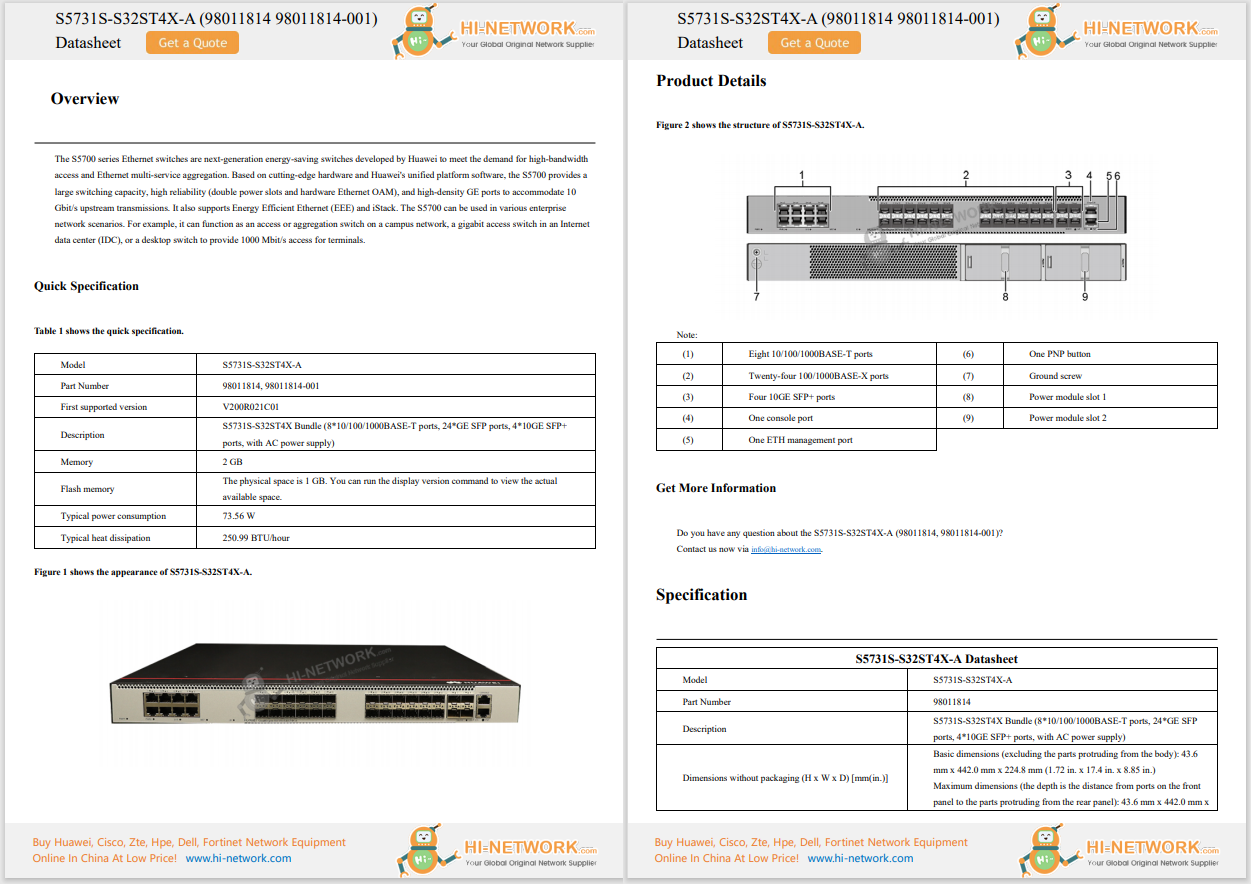











Chinese AI start-up DeepSeek has revealed that its theoretical profit margins could reach 545 percent, shedding light on the financial potential of its innovative approach to AI. The Hangzhou-based company said its V3 and R1 models' cost-to-sales ratio during 24 hours in February highlighted the massive profitability of its AI services.
However, DeepSeek clarified that actual revenues are much lower, as many services remain free or discounted during off-peak hours, and the calculations exclude research and development costs. Despite the hypothetical nature of these margins, the disclosure comes as AI start-ups worldwide struggle to prove their business models can turn sustainable profits.
Giants like OpenAI and Anthropic experiment with various revenue streams - from subscriptions to licensing fees - while investors increasingly question how soon these companies can achieve lasting profitability. What makes DeepSeek stand out is its commitment to transparency and open-source innovation.
The company publicly shared insights into its infrastructure, explaining how it optimises server loads, reduces latency, and maximises data processing efficiency. This openness contrasts sharply with many US-based competitors' secretive, proprietary strategies, signalling DeepSeek's confidence in its long-term vision.
In an industry racing to build more powerful AI, DeepSeek's willingness to share its methods and potential profitability sparks an important debate: Can a balance between innovation, openness, and sustainable revenue reshape the future of AI?
For more information on these topics, visit diplomacy.edu.
, Горячие метки:
Искусственный интеллект
В целях развития
Экономический и социальный совет
DeepSeek publish
Горячие метки:
Искусственный интеллект
В целях развития
Экономический и социальный совет
DeepSeek publish